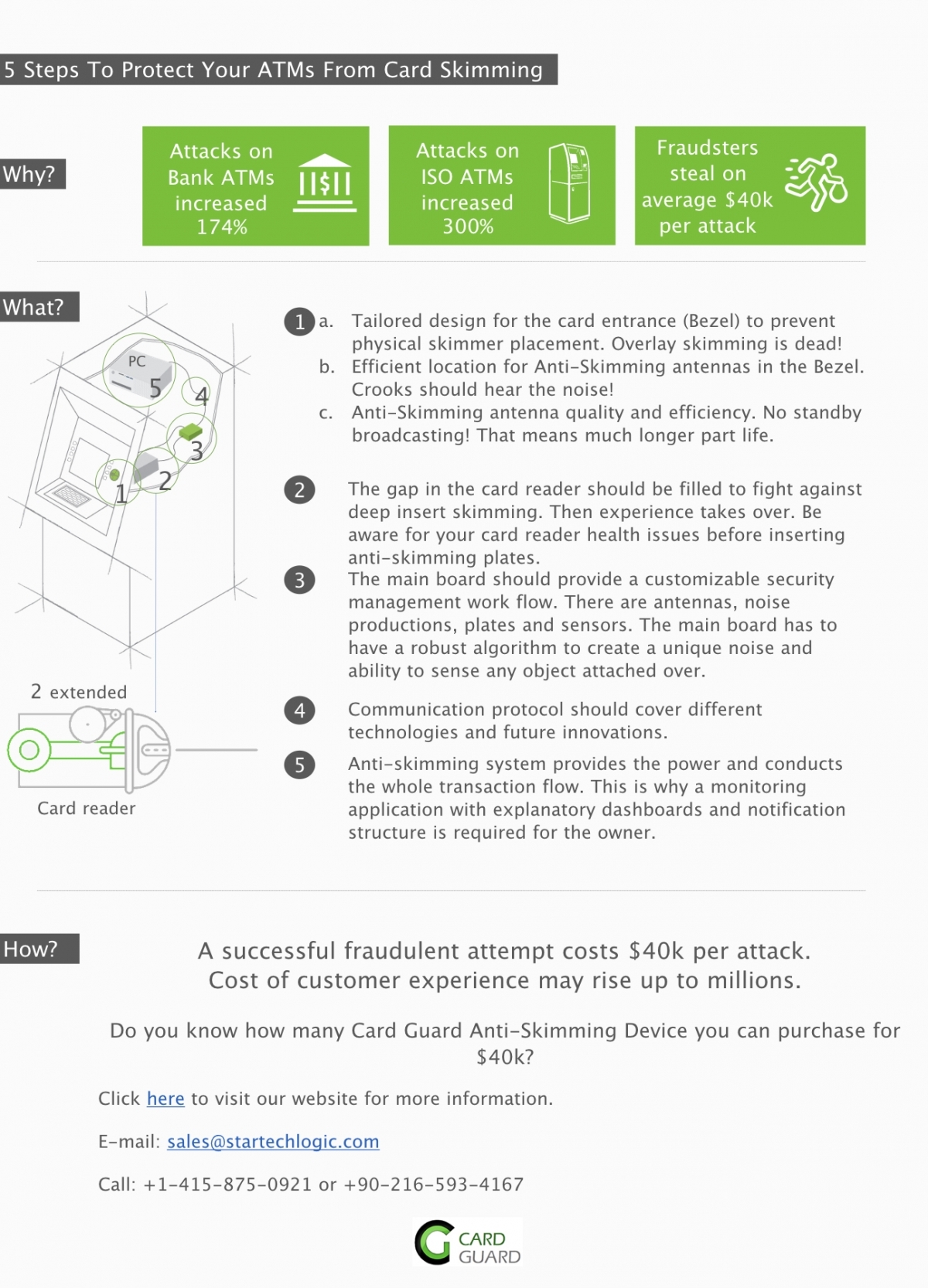
There are various points to be considered in ATM anti-skimming solutions. Unless all parts meet with requirements, solution remains vulnerable against skimming attacks.
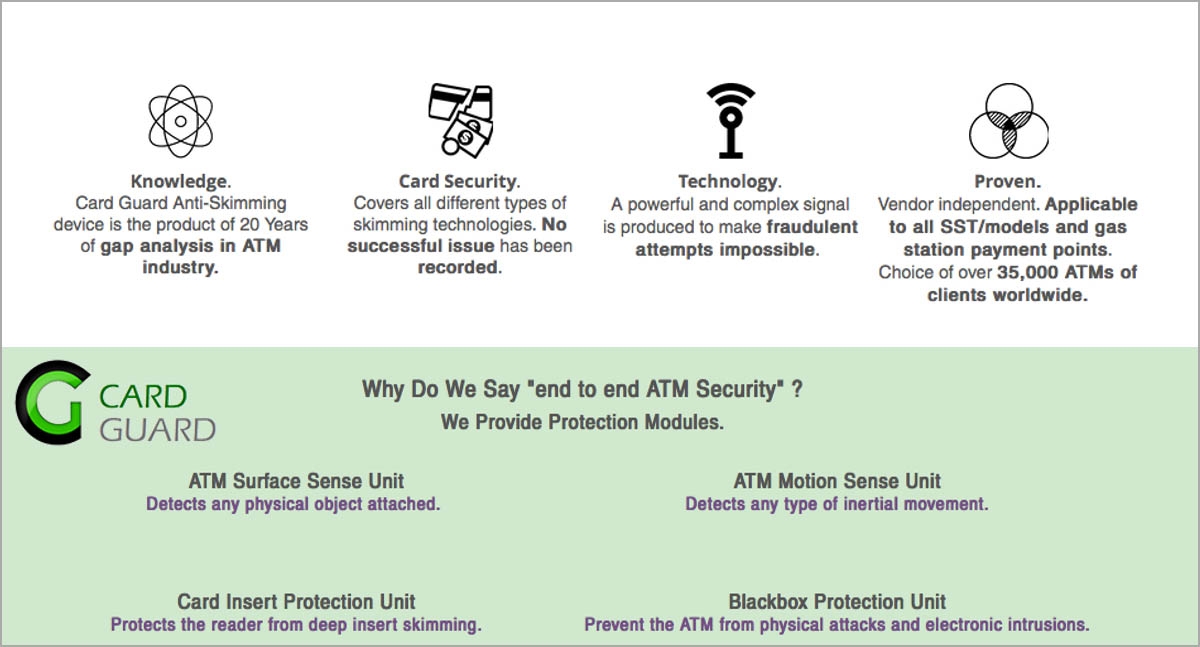
Anti-Skimming solutions are made up of 2 units. Software and Hardware protection units. Manufacturer has to have a decent knowledge of ATM and its detailed technical use cases. This creates a crucial advantage when it comes to solve a security gap in an ATM for card skimming.
It is significant to know that providers have a variety of service in ATM industry. Primary focus should be to have high-quality products and services with minimum cost and timing.
The solution should have been proved in different countries. It would have been an indicator such that how many products have been installed in different countries and regions.

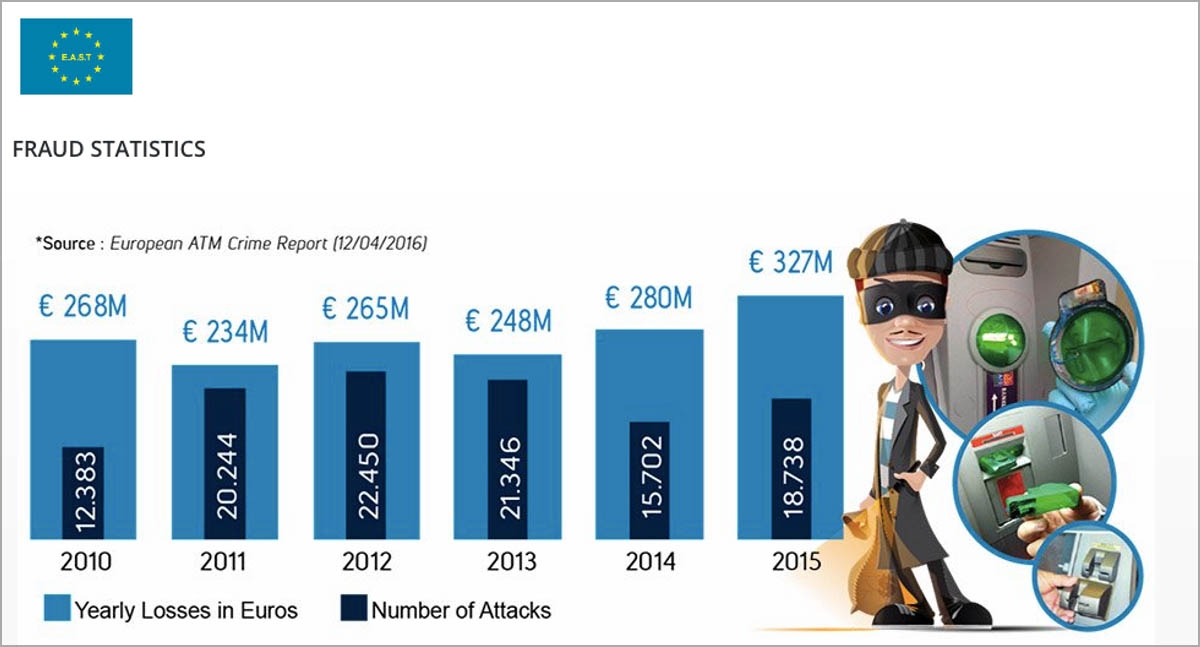
ATMs are under great risk of fraudulent attempts.
Only in EU. region, average loss in past 10 years is more than
300 million Euros per year.
Number of ATM fraudulent attempts have been increased by %450 worldwide since 2004. Average cost per successful ATM fraud attempt is $23,000.
Card Guard ATM
Anti-skimming solution provides limitless safety for each attempt.
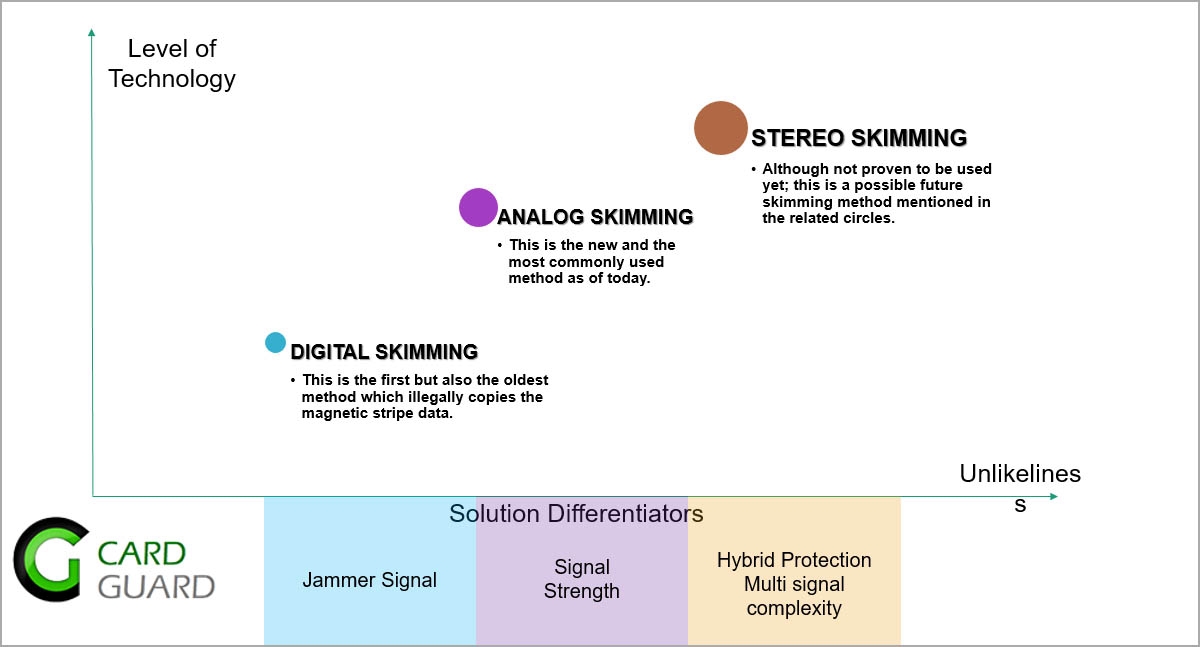
Solution should cover all existing and potential attacks. If crooks get ahead with a unique method, your provider should be able to cover your gaps with minimum cost and ultimate timing.
On the software protection unit: A unique noise production with algorithm based frequency and strength is required. Sensors listen your ATMs and Payment Points to protect against card skimming.
On the physical protection unit: Tailored and unique design solutions for card entrance (FDIs) has to be offered to prevent physical skimmer placement.
Provider should have various solution offerings covering deep insert skimming, overlay skimming, long bezel skimming, and more others.
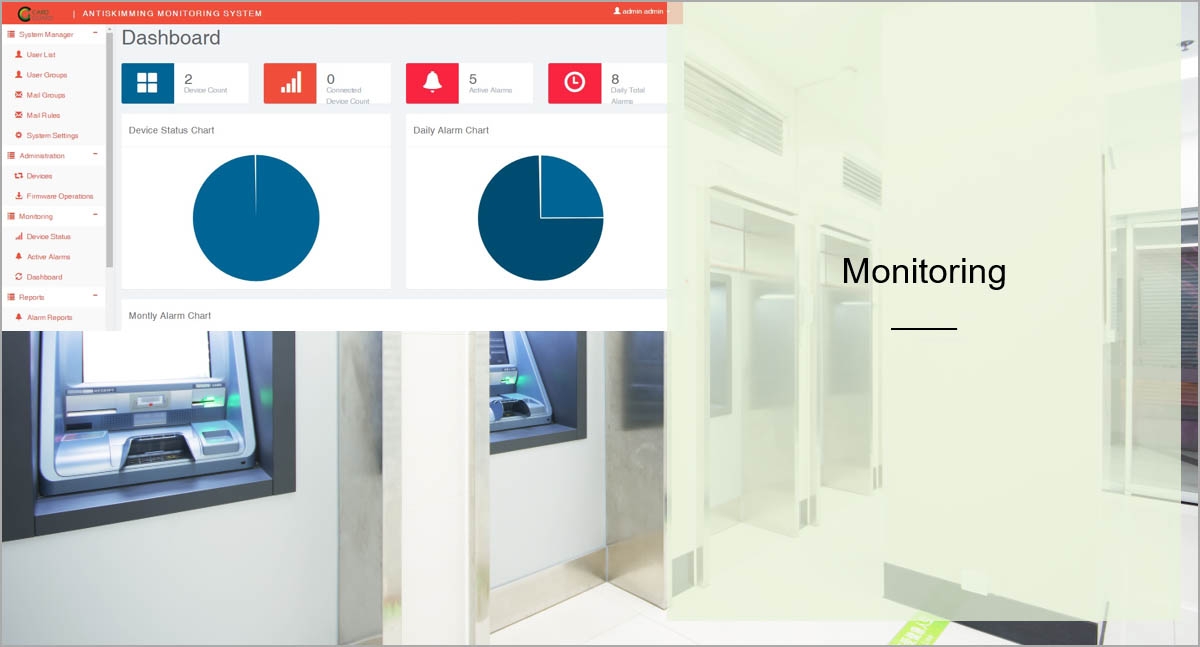
System needs to provide log files and comprehensive statistics for you to monitor events at your payment points/ATMs. Comprehensive dashboards and notifications are also crucial.
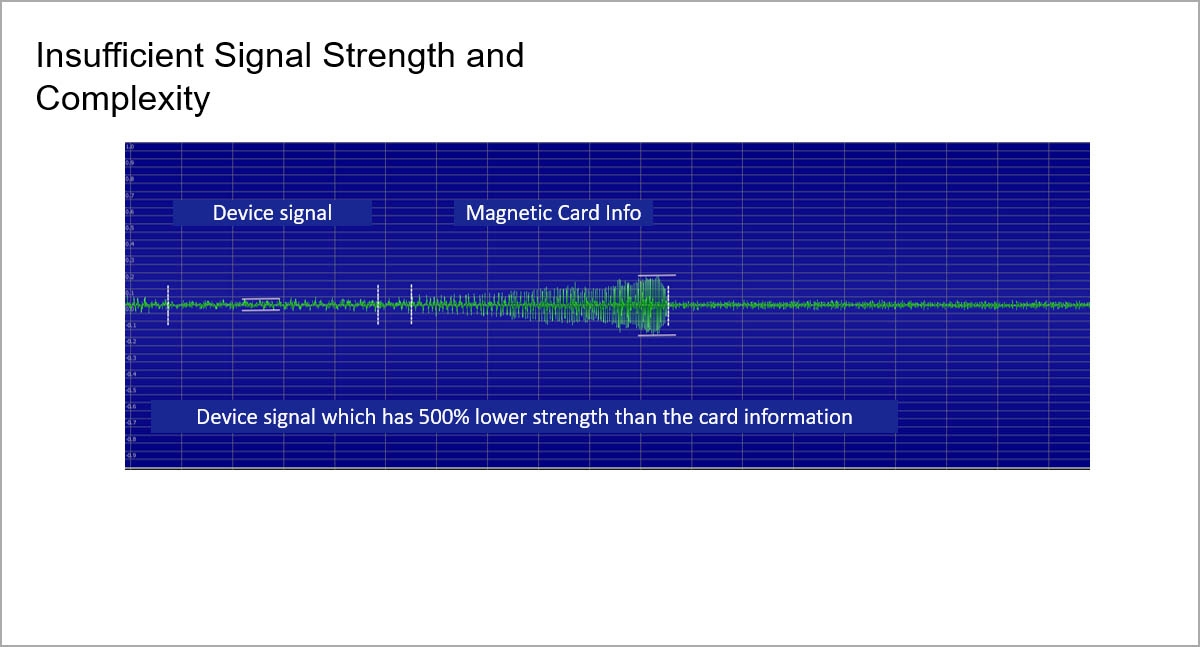
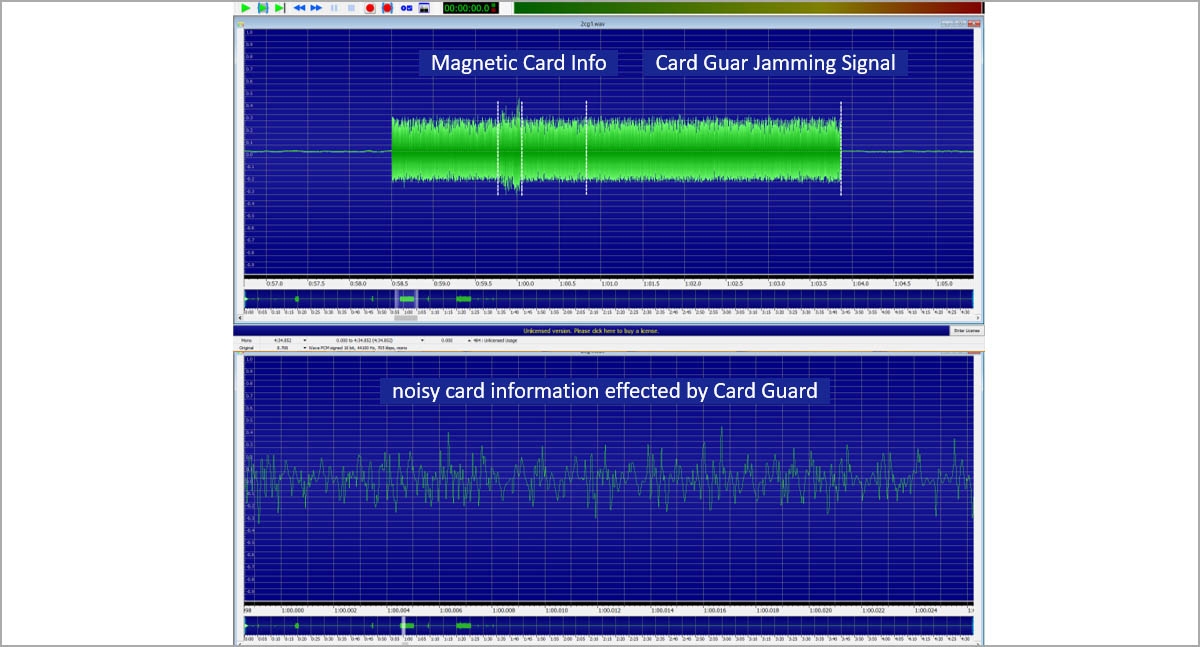
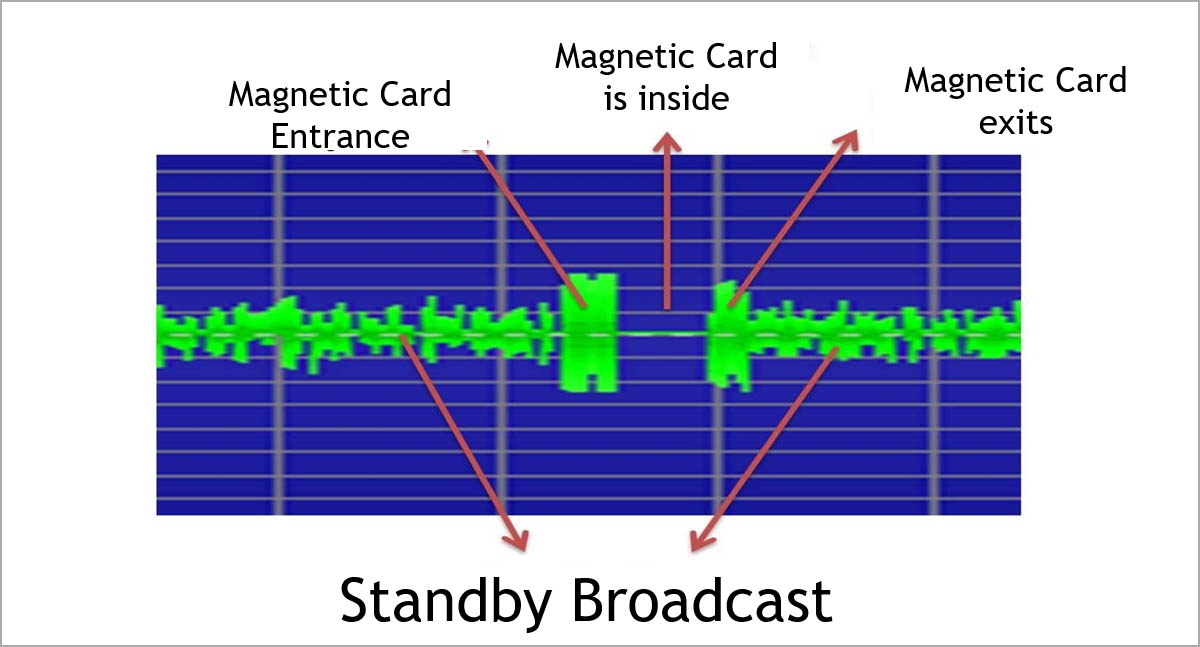
As seen in the figure, CPK 2nd version produces a low level standby signal. Strength of the signal increases as the card enters and leaves the card reader.
Continuous broadcasting shortens the life span of the parts including antennas and drivers managing these antennas.

During the measurements, it has been reported that within couple milimeters, signal strength of the CPK device decreases with an immense rate. This could have been a major problem for overlay skimming instances.
Copper wires wrapped around the bobins of antennas should have been thick and frequent enough to compensate signal distance sensitivity.

Metal sensor is not sufficient to detect all kinds of skimming devices. Other than metal, these sensors should be able to detect all kinds of various alloys and materials such as plastic.
Automatic calibration of sensors creates security gaps as it is more likely to be effected by temporary surroundings and produces false alarms. Most of the banks are suffering from the downtimes related to the false alarms. Manual calibration has been much more secure and reliable.

Look forward to discuss more.